Pressured by inflationary increases in food, labor, and other costs, operators of quick-serve restaurants are forced to raise menu prices and risk the chances of losing sales.
Quick-service restaurants seldom have the ability to hide price increases in the so-called “temporary” fees that are growing more common at full-service restaurants, and there’s a limit to the number of ways to reduce portion sizes to protect profit margins. Price-sensitive customers, feeling inflationary pressures themselves, are likely to push back when they see menu prices rise.
Clever restaurant owners and managers, however, are able to dodge pressure to raise prices by adopting AI-powered tools instead, which allow them to control operating costs. Best of all, savings from the adoption of new technologies will continue long after today’s wave of price inflation recedes.
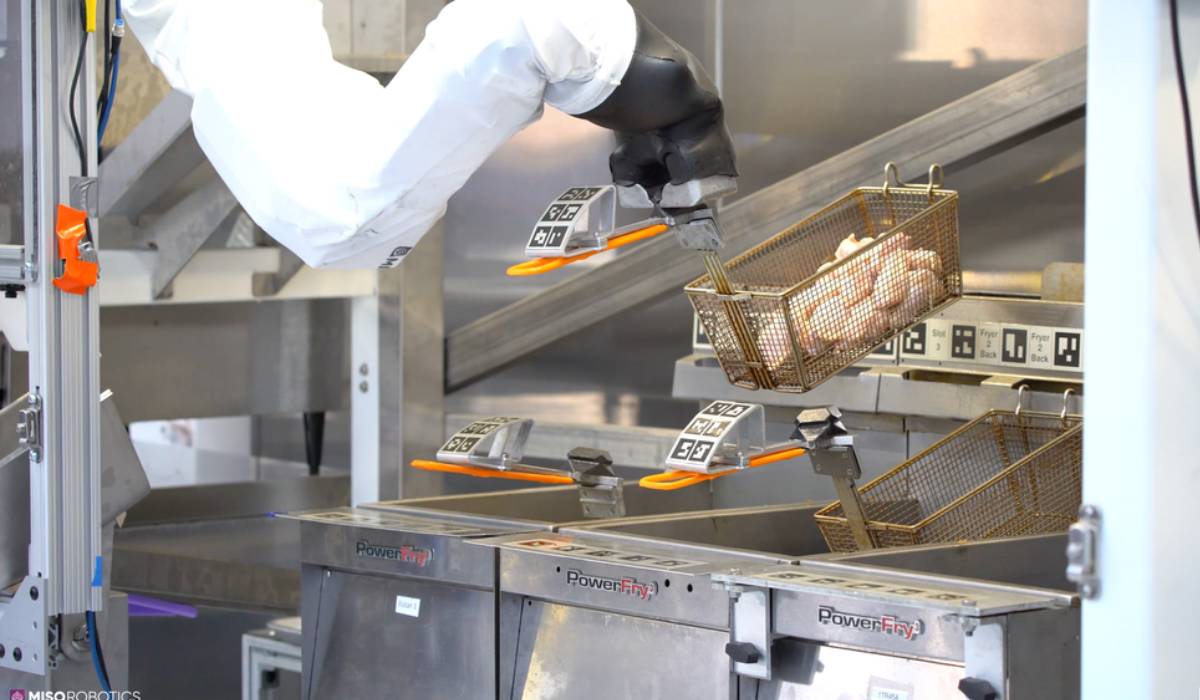
While futuristic hamburger-flipping robots have drawn much attention in the media, artificial intelligence is driving important cost-savings in more routine applications.
Improved appliance maintenance
One area where quick-service restaurants should focus on is the repair and maintenance of commercial kitchen equipment. The restaurant industry spends $28 billion a year to keep kitchen appliances operating, and when kitchen equipment is down, the lost revenue is estimated at $46 billion industry wide.
Downtime is dramatically reduced as new applications driven by artificial intelligence focus on prescriptive maintenance. Prescriptive maintenance is a maintenance concept that collects and analyzes data about an equipment’s condition to come up with specialized recommendations and corresponding outcomes to reduce operational risks. The purpose is to resolve issues before they become a problem while promising cost savings over routine or “time-based” preventive maintenance, because tasks are performed only when warranted.
Even though kitchen equipment has grown more sophisticated, repair-and-maintenance strategies have remained stagnant for decades. Restaurants continue to rely on the accumulated expertise of veteran repair technicians to find and solve problems. When those veteran technicians retire or move into other jobs, the lesser-skilled new workers who replace them don’t have the same wealth of experience. They need more time to complete routine maintenance jobs, and they are slower to get out-of-service equipment back up and running.
Service intelligence is a new AI-powered technology that shares the accumulated expertise of experienced veteran technicians who specialize in commercial kitchens. Even novice technicians have the benefit of knowledge accumulated over 25 or 35 years. With their smartphones, they walk step-by-step through the diagnosis and solution of all sorts of problems on both cold-line and hot-line appliances. With all that experience available to them, technicians identify the root of the problem more quickly, get the parts they need and return the equipment back into operation as soon as possible.
The new service intelligence technology helps with recruitment too. Young workers expect to find best-in-class technology at their workplace, and they gravitate to the employers who provide it.
AI-based tools allow restaurant owners to experience subtle, yet consistent savings within their repair budgets: When kitchen equipment is maintained more thoughtfully, it operates more efficiently. Better analysis helps predict and prevent problems. The hassles and costs associated with out-of-service equipment are reduced because problems are resolved more quickly. Even service technicians with only a few weeks on the job spend less time on fixes and have the knowledge to solve the issue the first time.
Improved purchasing decisions
Equipment repair and maintenance isn’t the only routine task where artificial intelligence is beginning to bring significant savings to quick-serve restaurants.
Applications that integrate point-of-sale (POS) information from customer transactions with purchasing inventory management, for instance, make a substantial difference in food costs. The applications track historical inventory, purchasing data from the past, and recent customer buying trends. Some even factor in possible surges in customer traffic from nearby special events. Recommendations ensure that the right amounts of foods are purchased, reducing the problems of out-of-stock ingredients. Less food is wasted, reducing the amount of working capital that’s tied up in food inventories and improving operating margins.
Other quick-serve management teams use AI-driven tools to create menus that maximize profits. The precise cost of each menu offering is calculated by the software, which then gathers additional information about the popularity of each item. When those two streams of data are combined, management teams and owners identify the stars of their menus—the popular items that don’t cost much to make—as well as the items that don’t carry their weight.
That’s information that allows menus to be reshaped—unwanted items can be dropped for more popular and higher grossing items. Kitchen staffers no longer need to learn preparation of low-performing items, and working capital isn’t tied up in inventory to create low-demand, low-margin items.
Improved staff recruitment
AI tools also help resolve the staffing issues that have been a major headache for quick-service managers since the start of the pandemic, needing a solution now more than ever.
AI-based recruitment tools help restaurants sort through the pool of potential new hires. By allowing job-seeking candidates, for instance, to submit resumes or other employment documents by text message, the AI-based tools can scan resumes quickly and evaluate candidates to find the best possible fits for their staffing needs. AI technology can also help restaurants find available talent more quickly by moving candidates through the recruitment process efficiently, instead of screening individual candidates one at a time, and scheduling individual interviews for each. Restaurant managers are not HR experts and those who don’t feel they have the skills to conduct a good interview no longer have to worry. The AI has it under control. In the end, these AI tools result in better candidates who are more likely to become skilled long-term employees, reducing future recruitment headaches while building a more efficient operation.
Today’s inflationary environment presents a major challenge to the quick-service restaurant industry. When competitors raise prices and inevitably experience declining customer loyalty, the managers who use AI technology to tighten their costs will be well-positioned to gain market share.
Profits aren’t protected by simply raising prices; control of operating costs is equally important. In any competitive industry, low-cost producers always have the advantage. Today’s AI-based tools provide the valuable assistance quick-service teams need to get serious about controlling their costs.
Sidney Lara is currently the Service Principal at Aquant, a software company focused on bringing service intelligence to field service organizations through AI and data-powered platforms. Sidney is passionate about eliminating waste from business processes and focusing on the activities creating value for customers. Prior to joining Aquant, Sidney worked fo RATIONAL USA as Vice President of Service.